Lake Urmia
Syllabus: GS1/Places in News
In News
- Iranian authorities have resorted to cloud seeding to induce artificial rainfall over the Lake Urmia basin amid Iran’s worst drought in decades.
About Lake Urmia
- It is situated in the Azerbaijan region of northwestern Iran and lies between East Azerbaijan and West Azerbaijan provinces.
- High evaporation rates make it extremely saline.
- It is the largest lake in the Middle East.
- Designated a Ramsar wetland and UNESCO Biosphere Reserve, the lake has shrunk dramatically since the 1990s.
Source: AIR
Rafah border
Syllabus:GS1/ Places in news, Geography
News
- Israel has reopened the Rafah border crossing between Gaza and Egypt for limited civilian movement after months of closure.
- The crossing has largely been closed since the Gazan side was captured by Israeli forces in May 2024.
Why is Rafah important to Gaza?
- Location: Rafah border is located on the Gaza–Egypt border, which was recognized by the 1979 Egypt–Israel peace treaty.
- Significance: The Rafah Border Crossing or Rafah Crossing Point is the sole crossing point between Egypt and the Gaza Strip.
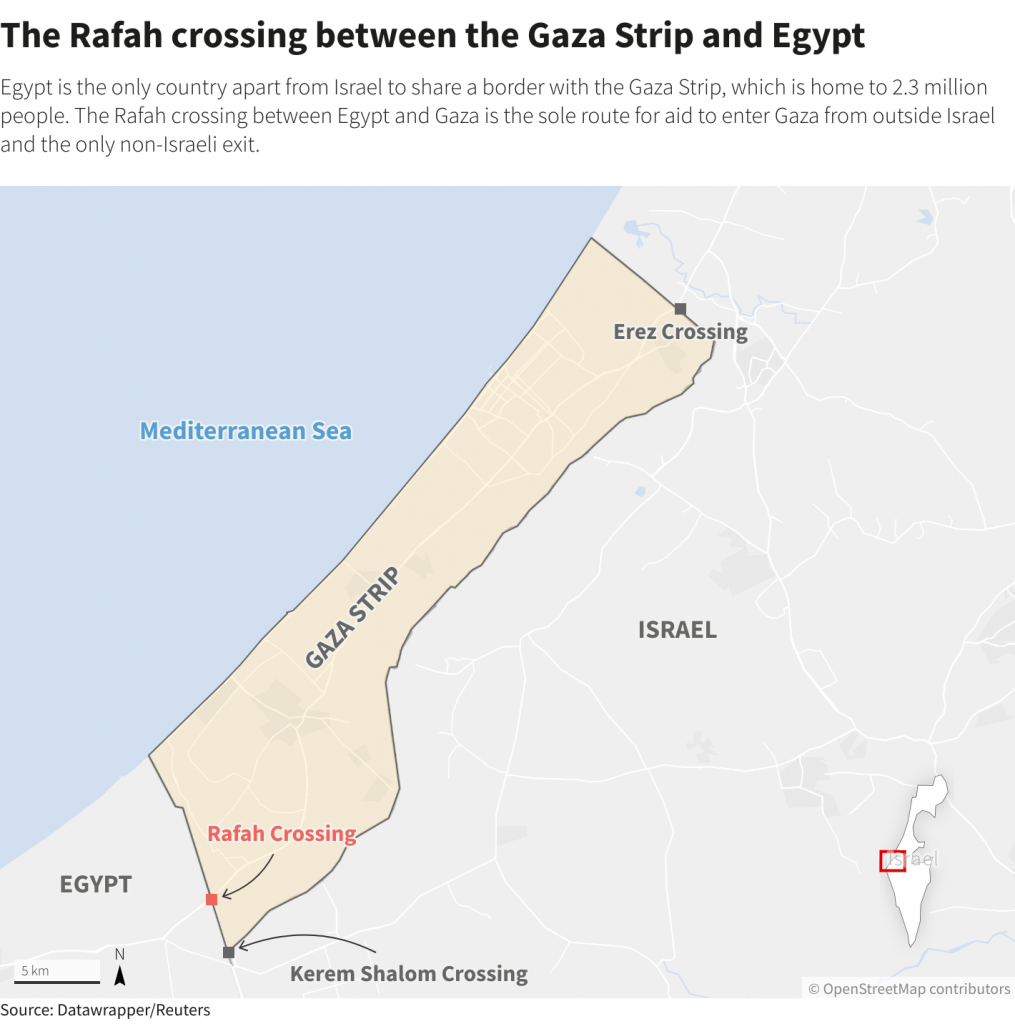
Source: BBC
President’s Rule Ends in Manipur
Syllabus: GS2/Polity and Governance
Context
- The President’s rule in Manipur was revoked and Yumnam Khemchand Singh sworn in as Chief Minister of Manipur.
Article 356 of the Constitution
- Article 356 empowers the President of India to impose President’s Rule in a state when governance cannot be carried out as per constitutional provisions.
- This typically follows a report from the Governor, stating that the state machinery has failed.
- The President issues a proclamation that transfers the state government’s functions to the Centre and the state legislature’s powers to Parliament.
- The judiciary, especially the High Court, continues to function without interference.
- The proclamation remains valid for up to two months but must be approved by both Houses of Parliament to extend further.
- If approved, the Rule can last for six months and be extended in increments of six months, up to a maximum of three years.
President’s Rule in India
- Since the adoption of the Constitution, Article 356 has been invoked over 130 times across various states and Union Territories.
- Manipur has witnessed the imposition of President’s Rule the highest number of times. However, some states and UTs have spent longer durations under central control than others.
- For example, Jammu and Kashmir or Punjab have had fewer instances but longer periods of President’s rule due to specific circumstances like prolonged political instability or security concerns.
S R Bommai v Union of India (1994) Case
- The Supreme Court, in the landmark S R Bommai v. The Union of India case placed restrictions on the misuse of Article 356.
- The judgment established that;
- The President’s decision is subject to judicial review.
- Courts can strike down the imposition if found illegal, malafide, or based on extraneous considerations.
- The state legislature alone would be suspended, and the executive and other arms of governance would continue unless Parliament ratified the proclamation within two months.
Emergency Provisions
- Part XVIII of the Constitution speaks of emergency provisions.
- The emergency provisions can be classified into three categories:
- Articles 352, 353, 354, 358, and 359 relate to National emergency,
- Articles 355, 356, and 357 deal with the imposition of President’s rule in States in a certain situation and,
- Article 360 speaks of financial emergency.
Source: TH
FORGE Initiative
Syllabus: GS2/ IR
In News
- India has expressed support for the FORGE Initiative at the inaugural Critical Minerals Ministerial hosted by the United States in Washington DC.
What is the FORGE Initiative?
- FORGE is a multilateral international cooperation framework aimed at de-risking global critical mineral supply chains by bringing together like-minded countries.
- It has been created as a successor to the Minerals Security Partnership (MSP).
- Core Idea is to reduce over-dependence on a few dominant suppliers, build trusted, transparent and resilient critical mineral ecosystems
India’s Alignment with the FORGE Initiative
- India sees FORGE as complementary to its domestic efforts such as:
- National Critical Minerals Mission (NCMM)
- Rare Earth Corridors
- Focus on self-reliance with global cooperation
Why FORGE Matters for India?
- Reduces import vulnerability
- Supports clean energy and EV goals
- Strengthens India’s role in global supply chains
- Enhances strategic partnerships with the US and other countries.
Source: AIR
Advance Pricing Agreement (APA)
Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
Context
- The Union Budget 2026-27 introduced a fast-track Unilateral Advance Pricing Agreement (APA) process for IT services, aiming for completion within 2 years, with an optional 6-month extension.
What is an Advance Pricing Agreement?
- APA is a binding agreement between a taxpayer and the tax administration that predetermines the arm’s length price (ALP) or the pricing methodology for international transactions for a specified future period.
- Legal Framework in India: The APA regime in India was introduced under Sections 92CC and 92CD of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
- The Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) is the competent authority for administering APAs.
Types of APAs
- Unilateral APA: An agreement involving only the taxpayer and the tax authority of their home country.
- Bilateral APA: An agreement involving the taxpayer, Indian tax authority, and the tax authority of the foreign country concerned.
- It provides protection against double taxation.
- Multilateral APA: Involves multiple countries and their respective tax authorities for complex, multi-jurisdictional transactions.
Significance of APA for India
- APAs help in reducing prolonged tax litigation, which has been a major concern for foreign investors.
- They promote a non-adversarial tax regime, aligning with India’s objective of stable and predictable taxation.
- APAs support India’s efforts to position itself as a trusted destination for global services and digital economy operations.
Source: TOI
Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS)
Syllabus: GS3/Agriculture
Context
- The Government’s initiative to transform Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) into multipurpose entities has significantly strengthened rural economic activity across the agriculture, dairy and fisheries sectors.
About
- PACS are the grass root level arms of the short-term co-operative credit structure.
- It is registered under the State Cooperative Societies Act (or Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, 2002 where applicable).
- PACS deals directly with the rural (agricultural) borrowers, give those loans and collect repayments of loans given and also undertake distribution and marketing functions.
- They occupy a predominant position in the co-operative credit structure and form its base.
- It serves as the final link between the ultimate borrowers on the one hand and the higher financing agencies, namely the Scheduled Commercial Banks, and the RBI/NABARD on the other hand.
- Ministry: Ministry of Cooperation.
Organisational Structure of PACS
- General Body of PACS: Exercise the control over board as well as management.
- Management Committee: Elected by the general body to perform the work as prescribed by the society’s rules, acts, and by-laws.
Source: PIB
Sarus Cranes Census data
Syllabus: GS3/Environment
In News
- The population of sarus cranes in Uttar Pradesh has gone up by 634 or 3.1% in a year, as per a government census.
Sarus crane
- It is the tallest flying bird in the world standing 152-156 cm tall with a wingspan of 240cm.
- Nature: It is a social creature, found mostly in pairs or small groups of three or four. Known to mate for life with a single partner, its breeding season coincides with heavy rainfall in monsoon.
- Habitat and Distribution: The Sarus habitat is outside protected areas, in natural wetlands with low water depth, marshy and fallow areas and agricultural fields.
- The Sarus crane has three disjunct populations in the Indian sub-continent, south-east Asia and northern Australia.
- In the Indian subcontinent, it is found in northern and central India, Terai Nepal and Pakistan.
- It was once a common site in the paddy fields of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Rajasthan, West Bengal, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh and Assam.
- But now it is mainly concentrated in Uttar Pradesh.
- The Sarus crane has three disjunct populations in the Indian sub-continent, south-east Asia and northern Australia.
- Ecological Role : They play a vital role in ecological balance by controlling the population of harmful insects and have significant cultural importance, while also being sociable. Sarus is omnivorous, feeding on fish and insects, as well as roots and plants.
- Protection status : Listed in Schedule IV of the Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972 and as Vulnerable on IUCN Red List
Source :HT
Exercise KHANJAR
Syllabus: GS3/Defence
Context
- The 13th edition of the India–Kyrgyzstan joint military exercise KHANJAR has begun in Sonitpur district of Assam.
About
- Exercise KHANJAR is an annual training event conducted alternatively between India and Kyrgyzstan since 2011.
- The previous edition was held in Kyrgyzstan in March 2025.
- The 14-day-long military exercise aims to enhance interoperability between the Special Forces of both nations, with a focus on joint operations in urban warfare and counter-terrorism scenarios under the United Nations mandate.
Source: AIR
Bharat Taxi
Syllabus: GS2/Government Initiatives
Context
- Union Minister for Home Affairs and Cooperation launched Bharat Taxi, India’s first cooperative-based ride-hailing platform.
About Bharat Taxi
- Bharat Taxi is a cooperative-led mobility platform registered under the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, 2002, and was established on June 6, 2025.
- The initiative aims to transform the mobility sector by placing drivers, referred to as sarathis, at the centre of ownership, operations, and value creation, offering an alternative to aggregator-based models.
- Drivers are also free to operate on other platforms without exclusivity clauses.
- The platform operates on a zero-commission and surge-free pricing model, with profits directly shared with drivers.
- It prioritises driver welfare through social security measures such as health insurance, accident insurance, retirement savings, and dedicated support systems.
- With over three lakh drivers and more than one lakh users already registered, Bharat Taxi aims to expand to all States and cities across India within the next two years.
Source: TH
Previous article
Strengthening Capital Goods Sector
Next article
Illegal Coal Mine Explosion in Meghalaya